 This SMR exercise is a variation of the Psoas Press and Iliacus Press techniques to address the Psoas muscle and Iliacus in the Hip Flexors in the front of your hips & core. You may find this exercise easier. If the Psoas Press or Iliacus Press are too intense to work with then practice the Iliopsoas Roll to more gently work out the "junk" in the front of your hips. It may take a month or two to help your muscles along to become healthy enough to handle the other two techniques (which are the preferred deep tissue SMR techniques for the iliopsoas group). If you have tightness or discomfort of the hip, knee, or lower back, then this exercise is likely to help. |
|
For written instructions, click here to download a printable PDF of the Iliopsoas Roll Be sure to post your questions and comments below. We want to provide the best instruction to help you recover from your workouts. Click here to return to all of the Fundamental SMR Techniques **All information is provided for educational purposes only. You should consult your doctor before attempting any exercises you read on this page or any page on this website.** |
Tag: Hip Flexors
Iliacus Press
 In addition using this technique to assist with issues in the front of your hips, if you have SI joint issues you should use this exercise to work out those deep knots in the muscles that attach in the FRONT that have a large influence on the function of the muscles in the BACK. If you have SI joint issues be sure you are practicing the Iliacus Press. The Iliacus muscle is part of the Iliopsoas Group, the most influential hip flexors in your body. If they are shot, nothing on the back of your body will work properly. |
|
For written instructions, click here to download a printable PDF of the Iliacus Press Downloadable video instructions coming soon! Click here to return to all of the SMR Techniques |
|
Be sure to post your questions and comments below. We want to provide the best instruction to help you recover from your workouts. **All information is provided for educational purposes only. You should consult your doctor before attempting any exercises you read on this page or any page on this website.** |
Fixing Ryan Moody’s Tight Hip
| In addition to being a talented and engaging presenter of the Explosive WOD Seminars, Ryan Moody is a heck of a jumper:
A good friend of his heard him speaking of a nagging hip issue and brought him to come visit us at the Rumble Roller booth at the CrossFit Games. After spending about 20 minutes with him and giving him some SMR "homework" to do each day, he got some rather dramatic results in only 2 days! |
Gluteus Minimus

Pictured above is the gluteus minimus muscle. It primarily works to extend (open) the hip. However, it has a small portion of muscle fibers that cross in front of the hip, so it can work as a weak hip flexor, too. If this muscle is overly tight then it is EXTREMELY LIKELY that you need to address the rectus femoris and the psoas (in that order).
The muscles are layered, showing how some of the muscles are covered by the others. All of the muscles are see-through so that you can appreciate the location and size of each muscle relative to the others. You can access individual muscle detail for all the other muscles in the body with our Coach membership.
Individual hip, lower back & thigh muscles you might be interested in: (any inactive links will be live soon)
Click here for a list of all the muscles.
Muscle that crosses the hip/lower back joint and crosses the hip/thigh joint (attaches to the spine and the femur)
Muscles that attach to the hip and the spine and/or ribs
- Rectus Abdominus
- External Abdominal Oblique
- Internal Abdominal Oblique
- Transverse Abdominus
- Latissimus Dorsi
- Iliocostalis Lumborum
- Longissimus Thoracis
- Quadratus Lumborum
- Multifidi
Muscles that attach to the hip and the thigh bone (femur)
- Iliacus
- Rectus Femoris
- Tensor Fasciae Latae
- Sartorius
- Gracilis
- Adductor Magnus
- Adductor Longus
- Adductor Brevis
- Pectineus
- Gluteus Maximus
- Gluteus Medius
- Gluteus Minimus
- Piriformis
- Superior Gemellus
- Obturator Internus
- Inferior Gemellus
- Obturator Externus
- Quadratus Femoris
- Biceps Femoris
- Semitendonosis
- Semimembranosis
Good luck working out those tight knots.
If you have any questions, please post a comment. We try to respond within 24 hours.
We're here to help you get more out of your training!
Sartorius

Pictured above is the sartorius muscle. It is nick-named the "carpenter's muscle." It primarily works as a stabilizer for the leg on the hip joint and rotates the knee outward. It is also a weak hip flexor. You can't move your hip in any direction without using this muscle. Persons that spend large amounts of time kneeling are likely to need stretching and SMR attention here.
80% of all adults over 18 years of age have some form of back pain. If you aren't also checking the psoas for excessive tension you are missing one of the most significant links to proper back function.
The muscles are layered, showing how some of the muscles are covered by the others. All of the muscles are see-through so that you can appreciate the location and size of each muscle relative to the others.
Individual hip, lower back & thigh muscles you might be interested in: (any inactive links will be live soon)
Click here for a list of all the muscles.
Click here to see the hip flexor muscles as a group.
Muscle that crosses the hip/lower back joint and crosses the hip/thigh joint (attaches to the spine and the femur)
Muscles that attach to the hip and the spine and/or ribs
- Rectus Abdominus
- External Abdominal Oblique
- Internal Abdominal Oblique
- Transverse Abdominus
- Latissimus Dorsi
- Iliocostalis Lumborum
- Longissimus Thoracis
- Quadratus Lumborum
- Multifidi
Muscles that attach to the hip and the thigh bone (femur)
- Iliacus
- Rectus Femoris
- Tensor Fasciae Latae
- Sartorius
- Gracilis
- Adductor Magnus
- Adductor Longus
- Adductor Brevis
- Pectineus
- Gluteus Maximus
- Gluteus Medius
- Gluteus Minimus
- Piriformis
- Superior Gemellus
- Obturator Internus
- Inferior Gemellus
- Obturator Externus
- Quadratus Femoris
- Biceps Femoris
- Semitendonosis
- Semimembranosis
Good luck working out those tight knots.
If you have any questions, please post a comment. We try to respond within 24 hours.
We're here to help you get more out of your training!
Iliacus

Pictured above is the iliacus. It is one of the hip flexor muscles, and pulls your leg up toward your hip (like when you lift your leg). It is one of the most influential muscle in the body. You can't move your hip in any direction without using this muscle. This muscle is VERY LIKELY to need some SMR attention along with the psoas muscle. 80% of all adults over 18 years of age have some form of back pain. If you aren't checking the psoas for excessive tension you are missing one of the most significant links to proper back function.
The muscles are layered, showing how some of the muscles are covered by the others. All of the muscles are see-through so that you can appreciate the location and size of each muscle relative to the others.
Individual hip, lower back & thigh muscles you might be interested in: (any inactive links will be live soon)
Click here for a list of all the muscles.
Click here to see the hip flexor muscles as a group.
Muscle that crosses the hip/lower back joint and crosses the hip/thigh joint (attaches to the spine and the femur)
Muscles that attach to the hip and the spine and/or ribs
- Rectus Abdominus
- External Abdominal Oblique
- Internal Abdominal Oblique
- Transverse Abdominus
- Latissimus Dorsi
- Iliocostalis Lumborum
- Longissimus Thoracis
- Quadratus Lumborum
- Multifidi
Muscles that attach to the hip and the thigh bone (femur)
- Iliacus
- Rectus Femoris
- Tensor Fasciae Latae
- Sartorius
- Gracilis
- Adductor Magnus
- Adductor Longus
- Adductor Brevis
- Pectineus
- Gluteus Maximus
- Gluteus Medius
- Gluteus Minimus
- Piriformis
- Superior Gemellus
- Obturator Internus
- Inferior Gemellus
- Obturator Externus
- Quadratus Femoris
- Biceps Femoris
- Semitendonosis
- Semimembranosis
Good luck working out those tight knots.
If you have any questions, please post a comment. We try to respond within 24 hours.
We're here to help you get more out of your training!
Hip Flexors
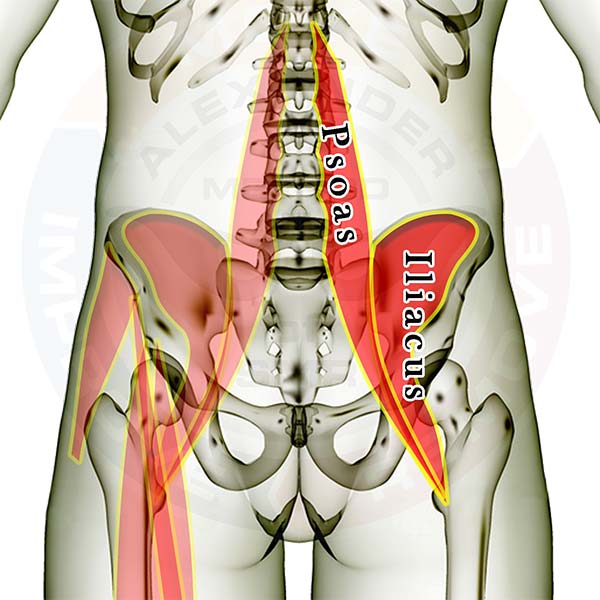
Pictured above are the hip flexor muscles. All of them pull your leg up toward your spine, and one of them pulls your spine toward your leg (like when you sit up). They are BY FAR the most influential group of muscles in the body. You can't move your hip or lower back in any direction without using one or more of these muscles. 80% of all adults over 18 years of age have some form of back pain. If you aren't checking your hip flexors for excessive tension you are missing the most significant group of muscles that contribute to proper back function.
The muscles are layered, showing how some of the muscles are covered by the others. All of the muscles are see-through so that you can appreciate the location and size of each muscle relative to the others. On the left side you can see the other muscles that are present in the same area as the hip flexors, and a couple muscles that act as mild hip flexors (Tensor Fasciae Latae & Sartorius).
Click here for a list of all the muscles.
Individual hip, lower back & thigh muscles you might be interested in: (any inactive links will be live soon)
Muscle that crosses the hip/lower back joint and crosses the hip/thigh joint (attaches to the spine and the femur)
Muscles that attach to the hip and the spine and/or ribs
- Rectus Abdominus
- External Abdominal Oblique
- Internal Abdominal Oblique
- Transverse Abdominus
- Latissimus Dorsi
- Iliocostalis Lumborum
- Longissimus Thoracis
- Quadratus Lumborum
- Multifidi
Muscles that attach to the hip and the thigh bone (femur)
- Iliacus
- Rectus Femoris
- Tensor Fasciae Latae
- Sartorius
- Gracilis
- Adductor Magnus
- Adductor Longus
- Adductor Brevis
- Pectineus
- Gluteus Maximus
- Gluteus Medius
- Gluteus Minimus
- Piriformis
- Superior Gemellus
- Obturator Internus
- Inferior Gemellus
- Obturator Externus
- Quadratus Femoris
- Biceps Femoris
- Semitendonosis
- Semimembranosis
Good luck working out those tight knots.
If you have any questions, please post a comment. We try to respond within 24 hours.
We're here to help you get more out of your training!
Psoas

Pictured above is the psoas. It is one of the hip flexor muscles, and pulls your leg up toward your spine (like when you lift your leg), or your spine toward your leg (like when you sit up). It is BY FAR the most influential muscle in the body. You can't move your hip or lower back in any direction without using this muscle. 80% of all adults over 18 years of age have some form of back pain. If you aren't checking the psoas for excessive tension you are missing one of the most significant links to proper back function.
The muscles are layered, showing how some of the muscles are covered by the others. All of the muscles are see-through so that you can appreciate the location and size of each muscle relative to the others.
Individual hip, lower back & thigh muscles you might be interested in: (any inactive links will be live soon)
Click here for a list of all the muscles.
Click here to see the hip flexor muscles as a group.
Muscle that crosses the hip/lower back joint and crosses the hip/thigh joint (attaches to the spine and the femur)
Muscles that attach to the hip and the spine and/or ribs
- Rectus Abdominus
- External Abdominal Oblique
- Internal Abdominal Oblique
- Transverse Abdominus
- Latissimus Dorsi
- Iliocostalis Lumborum
- Longissimus Thoracis
- Quadratus Lumborum
- Multifidi
Muscles that attach to the hip and the thigh bone (femur)
- Iliacus
- Rectus Femoris
- Tensor Fasciae Latae
- Sartorius
- Gracilis
- Adductor Magnus
- Adductor Longus
- Adductor Brevis
- Pectineus
- Gluteus Maximus
- Gluteus Medius
- Gluteus Minimus
- Piriformis
- Superior Gemellus
- Obturator Internus
- Inferior Gemellus
- Obturator Externus
- Quadratus Femoris
- Biceps Femoris
- Semitendonosis
- Semimembranosis
Good luck working out those tight knots.
If you have any questions, please post a comment. We try to respond within 24 hours.
We're here to help you get more out of your training!
Rectus Femoris

Pictured above is the most influential of the quadriceps, the rectus femoris. The leg on the right has the rectus femoris labeled. This is the only quadriceps that acts on the 2 largest joints in your body - the hip AND the knee. If this muscle goes dysfunctional with too many muscular knots, then all movements involving either of these two joints will be compromised. If you only have time for one SMR exercise, DO SMR FOR THE RECTUS FEMORIS! (It is that important.)
The leg on the left has all the muscles that cross your thigh in the region of the rectus femoris. All of the muscles in the left leg are see-through so that you can appreciate the location and size of each muscle relative to the others.
Click here for a list of all the muscles.
Click here to view the quads all together.
Additional Quads you might be interested in:
Good luck working out those tight knots.
If you have any questions, please post a comment. We try to respond within 24 hours.
We're here to help you get more out of your training!
The Quadriceps

Pictured above are the quadriceps. The leg on the right has each muscle labeled. The muscles are also layered just like in your thigh, showing how some of the muscles are covered by the others.
The leg on the left has all the muscles that cross the front of your thigh in addition to the quads. All of the muscles in the left leg are see-through so that you can appreciate the location and size of each muscle relative to the others.
Click here for a list of all the muscles.
Individual Quads you might be interested in:
Good luck working out those tight knots.
If you have any questions, please post a comment. We try to respond within 24 hours.
We're here to help you get more out of your training!

