Pictured above is the soleus muscle. It stabilizes your ankle and pulls your heel bone towards the back of your lower leg (plantar flexes your ankle). It attaches to most of the length of the back of both your lower leg bones from very near your knee to just above your heel bone, moreso on the fibula bone (the smaller outside bone) than the tibia (the large weight-bearing bone in the lower leg). It also attaches to the achilles tendon from the inside (the gastrocnemius muscle attaches to the achilles tendon from the outside).
If this muscle locks up, all action invloving the ankle will be compromised. It is EXTREMELY LIKELY to be the source of your lower leg troubles. If you have issues with shin splints, plantar fasciitis, toe pains, or anything involving the lower leg or foot, make sure you address the soleus during your stretching and SMR efforts. You may need to work other areas, but do not skip the soleus!
The soleus is displayed on the right leg. On the left leg the muscles are layered, showing how some of the muscles are covered by the others. All of the muscles are see-through so that you can appreciate the location and size of each muscle relative to the others.
Click here for a list of all the muscles.
Muscles that cross or attach to the hip or thigh bone (femur) and attach below the knee joint and DO NOT attach to the knee cap (patella)
Lower Leg
The following muscles attach across or below the knee.
Click the appropriate link for your interest.
Muscles that cross the knee
Muscles that pass or attach between the knee & ankle
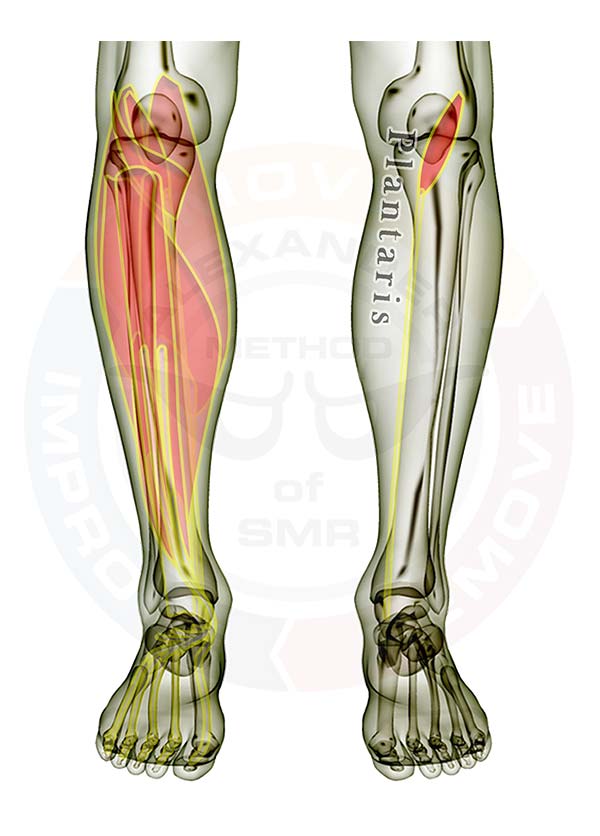
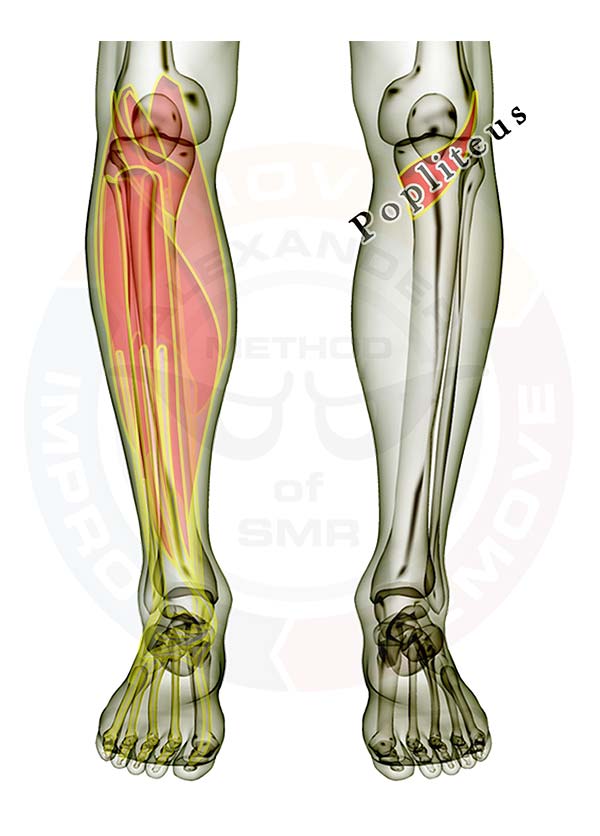
- Gastrocnemius
- Popliteus
- Plantaris
- Soleus
- Peroneus Longus
- Peroneus Brevis
- Flexor Digitorum Longus
- Flexor Hallucis Longus
- Posterior Tibialis
- Anterior Tibialis
- Extensor Digitorum Longus
- Extensor Hallucis Longus
Good luck working out those tight knots.
If you have any questions, please post a comment. We try to respond within 24 hours.
We're here to help you get more out of your training!