Pictured above are all the muscles in the bottom of the foot. As you can see there are MANY little muscles in the small area of your foot. It is best to approach the individual muscles initially as a group and shift attention to the forefoot, arch, or heel instead of starting with the individual muscles. If you find you need to go deeper to isolate one individual area or muscle take the process in stages. Releasing tension in the entire foot can allow you to more easily reach the specific muscle you wish to address.
With any foot issue it is wise to continually address the largest muscles that insert into your foot, the toe and arch muscles that originate in the calves.
Click here for a list of all the muscles.
Lower Leg
The following muscles attach across or below the knee. Click the appropriate link for your interest.
Muscles that cross the knee
Muscles that pass or attach between the knee & ankle
- Gastrocnemius
- Popliteus
- Plantaris
- Soleus
- Peroneus Longus
- Peroneus Brevis
- Flexor Digitorum Longus
- Flexor Hallucis Longus
- Posterior Tibialis
- Anterior Tibialis
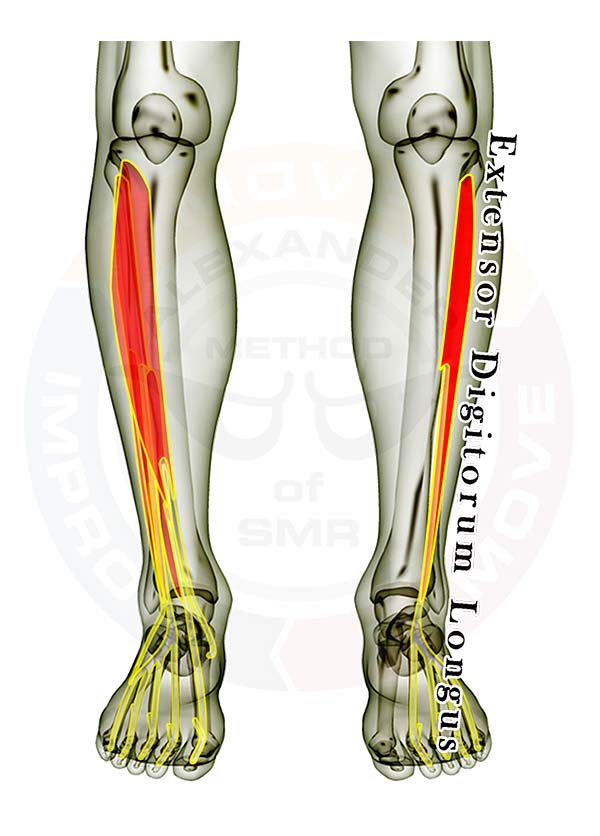
- Extensor Digitorum Longus
- Extensor Hallucis Longus
Muscles that cross the ankle
- Flexor Digitorum Longus
- Flexor Hallucis Longus
- Posterior Tibialis
- Peroneus Longus
- Peroneus Brevis
- Anterior Tibialis
- Extensor Digitorum Longus
- Extensor Hallucis Longus
Muscles in the bottom of the foot (active links coming soon)
- Flexor Digitorum Brevis
- Abductor Hallucis
- Abductor Digiti Minimi
- Flexor Hallucis Brevis
- Quadratus Planatae
- Lumbricals
- Adductor Hallucis
- Flexor Digitorum Minimi Brevis
- Plantar Interossei
Muscles in the top of the foot (active links coming soon)
- Extensor Digitorum Brevis
- Extensor Hallucis Brevis
- Dorsal Interossei
Good luck working out those tight knots.
If you have any questions, please post a comment. We try to respond within 24 hours.
We're here to help you get more out of your training!