Pictured above is the quadratus lumborum (QL). It is one of the deepest of the lower back stabilizers and it hikes your hip (pulls your hip up toward your spine).
It is commonly too tight in persons diagnosed with one leg longer than the other. You can't move your hip or lower back in any direction without using this muscle. 80% of all adults over 18 years of age have some form of back pain. If you aren't checking the QL for excessive tension you are missing one of the most significant links to proper back function.
The muscles are layered, showing how some of the muscles are covered by the others. All of the muscles are see-through so that you can appreciate the location and size of each muscle relative to the others.
Click here for a list of all the muscles.
Individual hip, lower back & thigh muscles you might be interested in: (any inactive links will be live soon)
Click here to see the hip flexor muscles as a group.
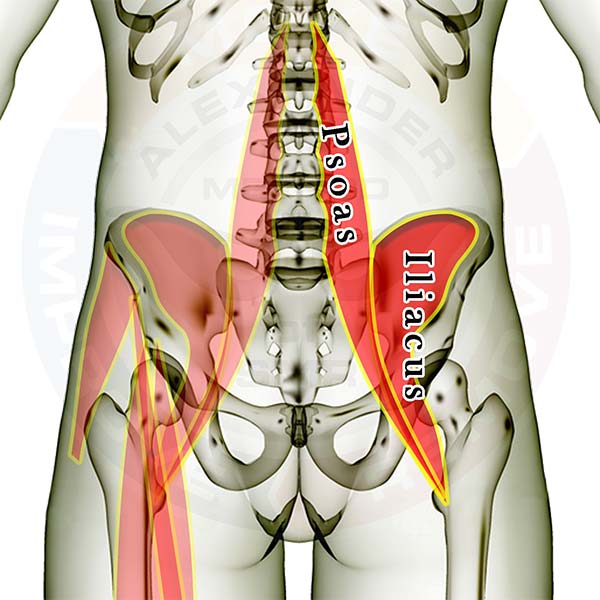
Muscle that crosses the hip/lower back joint and crosses the hip/thigh joint (attaches to the spine and the femur)
Muscles that attach to the hip and the spine and/or ribs
- Rectus Abdominus
- External Abdominal Oblique
- Internal Abdominal Oblique
- Transverse Abdominus
- Latissimus Dorsi
- Iliocostalis Lumborum
- Longissimus Thoracis
- Quadratus Lumborum
- Multifidi
Muscles that attach to the hip and the thigh bone (femur)
- Iliacus
- Rectus Femoris
- Tensor Fasciae Latae
- Sartorius
- Gracilis
- Adductor Magnus
- Adductor Longus
- Adductor Brevis
- Pectineus
- Gluteus Maximus
- Gluteus Medius
- Gluteus Minimus
- Piriformis
- Superior Gemellus
- Obturator Internus
- Inferior Gemellus
- Obturator Externus
- Quadratus Femoris
- Biceps Femoris
- Semitendonosis
- Semimembranosis
Good luck working out those tight knots.
If you have any questions, please post a comment. We try to respond within 24 hours.
We're here to help you get more out of your training!